Author(s): Petre Gâștescu,ELENA ŢUCHIU / Language(s): English
Issue: 2/2022
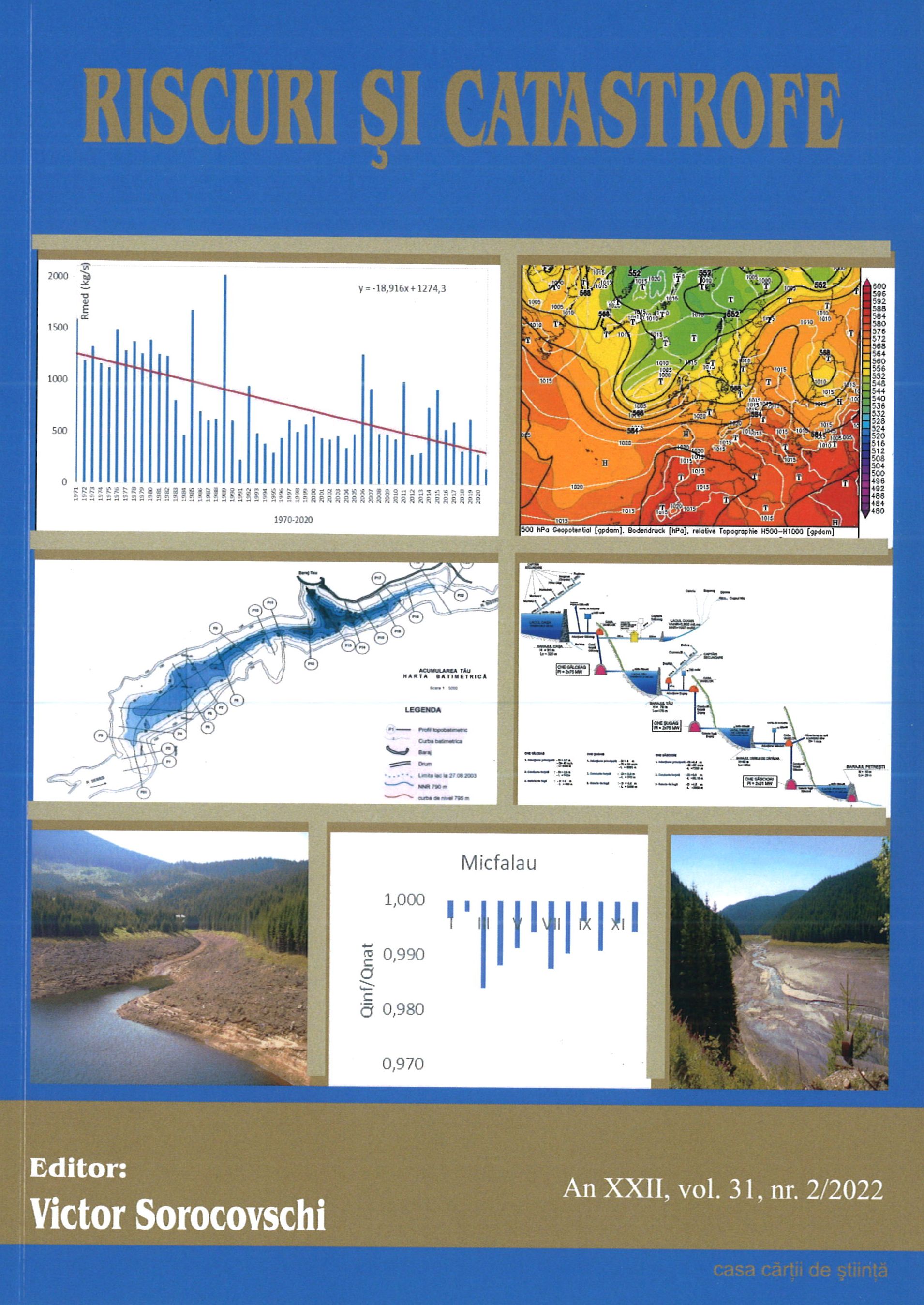
This paper provides an updated analysis of the Danube’s hydrographic, hydrologic, and water quality features describing the characteristics of its entire course and focusing on the lower sector. The Danube is the second largest watercourse in Europe in terms of length (2860 km) and basin area (817,000 km2). In Romania, the Danube is 1,075 km long and drains over 97% of the country’s territory.. The Danube’s multiannual average discharge increases downstream collecting the tributaries waters - 1,470 m3/s at Passau, after the confluence with the river Inn; 1,920 m3/s in Vienna; 2,350 m3/s in Budapest and 5,300 m3/s after the Drava, Tisa, and Sava confluences. The Danube enters Romania at Baziaş with 5,523 m3/s (multiannual average flow during the 1931-2020 period). The maximum discharge is recorded by the high spring waters, but occasionally in summer, too: 15,800 m³/s at Baziaș in April 2006; 15,300 m3/s at Giurgiu, and 15,900 m3/s at Ceatal Chilia. The minimum discharge occurs in autumn and occasionally in winter: 1,040 m3/s at Baziaș in 1949; and 1,790 m3/s at Ceatal Chilia in 1947. The suspended sediments discharge (1840-2000) was on average 53 million tons/ year at Isaccea, that is, 1,681 kg/s. Since 1996, the qualitative monitoring of the water has been implemented through the Danube Transnational Monitoring Network (TNMN) of the International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River (ICPDR). The spatial and temporal variation in the Pontic sector of the physical-chemical quality indicators, reflects the general characteristics and the effect/impact of the main pressures identified at the basin level for the 1996-2020 period, in monitoring stations (from Baziaș to Reni and on its 3 arms). From a complete and integrative perspective and in line with the Water Framework Directive provisions, the Danube water bodies, their typology, ecological status/potential, and chemical status have been presented. The lower Danube-associated natural protected areas that are established under the international, European and national legal requirements have been reviewed.
More...